Science
Science lessons at Roger Ascham will draw children’s attention to the world around them. They are encouraged to develop a sense of excitement and curiosity about natural phenomena and an understanding of how science can be used to explain, predict and analyse what occurs. Pupils will develop scientific knowledge and conceptual understanding; learn to work scientifically; and understand the uses and implications of scientific practice and discovery, the impact it has had in the past and its potential for the future.
Children learn about the world by experiencing and observing it. We encourage them to be curious and ask questions about the world, teaching them how to answer their questions through the use of scientific processes such as observing, pattern seeking, identifying, classifying and grouping, carrying out controlled investigations as well as research through the use of secondary sources. Children learn to design their own enquiries, aware of how to ensure that the outcomes of their tests are valid. They make predictions and draw conclusions, justified with the evidence they have collected.
Solving problems requires specific knowledge. Teachers will ensure that practical experiments deepen pupils understanding of scientific concepts by teaching the knowledge and skills required to understand the processes they are investigating. Each series of lessons will explain knowledge and concepts and also enable the children to enquire and learn through experience. In other words, our science curriculum aims to find the delicate balance between knowledge built by generations of scientists and scientific enquiry.
Children will need to draw upon their English and mathematical skills during science lessons, for example when researching, recording, presenting, taking accurate measurements as well as accessing and analysing data.
EYFS Learning Journey
Understanding Our World
Opportunities for scientific learning will also happen through play, eg. rolling cars down a ramp. Children may predict which will go faster and explain reasons for their prediction. Fair testing can be modelled and predictions re-visited.
Scientific Enquiry

Regular scientific experiments will take place in a range of curriculum subjects, eg. the Mentoes and fizzy drink experiment may be used to teach the ‘zz phoneme in phonics or to make fireworks when learning about bonfire night.
Animals Including Humans

We will learn about life cycles (also linked with seasonal changes). Children explore these through picture books and models as well as seeing it happen in ‘real life’ eg. ‘Living Eggs’.
Growing

This is linked closely with the seasonal changes. Children will observe the falling of the leaves in winter and then the blossom in the spring. They will plant seeds and bulbs in their gardens and learn to care for them.
Seasonal Changes

Throughout the year, children will be encouraged to notice the seasonal changes around them and record what they see through a range of mediums (art, photography / IT, poetry writing).
Years 1 & 2 Learning Journey
Year 1
Seasonal Changes

In this topic, children will learn about the four seasons. Children will learn what the word weather means and find out how different types of weather can be measured. Children will use a class weather station to observe measure and record the weather across the seasons. They will also observe changes across the seasons by exploring the signs of autumn, winter, spring and summer through nature and wildlife. Children also work scientifically by observing, collecting, recording and interpreting simple data.
Everyday Materials

Here we will learn about everyday materials including wood, plastic, metal, water and rock. Children will learn to identify and name everyday materials and will have the opportunity to explore the properties of these materials. They will also carry out a simple investigation to help them decide which material would be most suitable to use for an everyday object such as an umbrella. Children will apply their knowledge of everyday materials to sort objects by their properties. A range of scientific skills are used including, discussions, labelling and matching activities, games, and an investigation to encourage children to ask and find the answers to questions.
Animals Including Humans

In this topic, we will learn about five of the groups that scientists use to classify animals: mammals, fish, birds, reptiles and amphibians. They will learn to identify the group an animal belongs to by its features and will classify animals according to their group. They will also learn about the different diets animals eat. Children will learn about the parts of the human body and will have the opportunity to explore the five senses through a simple investigation.
Plants

In this topic, children will learn to name the basic parts of a plant, including seeds. They will have the opportunity to plant their own seeds and to make observations of how they grow over time. Children will also learn to identify, name and describe a variety of garden and wild plants as well as evergreen and deciduous trees. Finally, the children will use all of their knowledge gained throughout the topic to identify, compare and classify plants.
Year 2
Animals Including Humans

In this topic, children will begin by looking at young animals and comparing them to their adults. They will look at how animals change as they grow up and be introduced to the life cycles of several varied common animals, including humans. They look in detail at how humans change as they grow older, drawing on their own observations. Children are introduced to the three basic needs of animals for survival (water, food and air). They will apply this knowledge, alongside research from secondary sources, to suggest ways to look after pets. The topic ends with children looking at healthy lifestyles, including the importance of exercise, healthy eating and hygiene. These healthy living lessons develop ‘working scientifically’ skills through investigating the impact of exercise on our bodies and how handwashing is essential for good hygiene.
Uses of Everyday Materials

Here we will learn about the uses of everyday materials including wood, plastic, metal, glass, brick, paper and cardboard. Children then go on to compare the suitability of different everyday materials for different purposes. They explore how objects made of some everyday materials can change shape and how the recycling process is able to reuse some everyday materials numerous times. It finishes with children learning about new discoveries which have been made over time with a specific focus on John McAdam. A range of scientific skills are used in including, discussions, debates, sequencing and a local walk where children work scientifically to identify the uses of everyday materials in the local area.
Living Things and their Habitats

In this topic, children we will learn learn about a variety of habitats and the plants and animals that live there. They learn to tell the difference between things that are living, dead and things that have never been alive, and apply this in a range of contexts. They make observations of a local habitat and the creatures that live there, investigating conditions in local microhabitats and how they affect the minibeasts found within them. This topic allows children to research a range of global habitats and how the living things that live there are suited to their environments, and also provides an introduction to the idea of dependency between plant and animal species.
Plants
In this topic, children will learn what plants need to stay healthy. They will have the opportunity to carry out their own investigations into what plants need to grow well. Children will also closely observe the inside of a seed and learn about the life cycle of a plant. They will also learn how plants look when they don’t get the things they need. Finally, children will learn how plants have adapted to live in different environments around the world.
Years 3 & 4 Learning Journey
Year 3
Rocks and Soils

In this topic, children will discover the different types of rocks and how they are formed. Children will compare and group rocks based on appearance and simple properties. They will learn how fossils are formed and learn about the contribution of Mary Anning to the field of palaeontology. Children will understand how soil is formed and then investigate the permeability of different types of soil.
Forces and Magnets
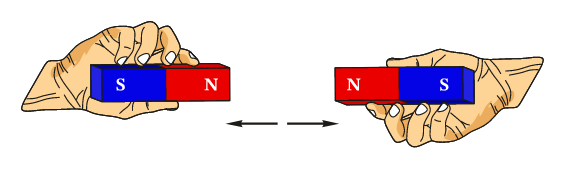
Here children will learn about forces, friction and magnetic attraction. They will learn about forces in the context of pushing and pulling, and will identify different actions as pushes or pulls. The children will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate friction, by exploring the movement of a toy car over different surfaces. They will work in a hands on way to identify magnetic materials. Furthermore, they will conduct an investigation into the strength of different types of magnet. The children will have the chance to explore the way magnetic poles can attract and repel in an exciting activity, making their own compass and using it to find hidden items. The children will use their understanding of magnetic attraction to design and create their own magnetic game. They will develop their scientific enquiry skills, making observations, predictions and conclusions.
Light

In this topic, children will learn about light, reflections and shadows. They will learn about different sources of light, and that we need light to see. The children will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate reflective materials, in the context of designing an object such as a new book bag. They will work in a hands on way playing a range of mirror games, finding out more about reflective surfaces. Furthermore, they will learn that the sun’s light can be dangerous, and will create an advert for a pair of sunglasses or a sun hat that they have designed. The children will have chance to test which objects are opaque in an exciting investigation such as to design the most effective curtains, and will find out how shadows change when the distance between the object and light source changes. They will develop their scientific enquiry skills by, making observations, predictions and conclusions.
Plants
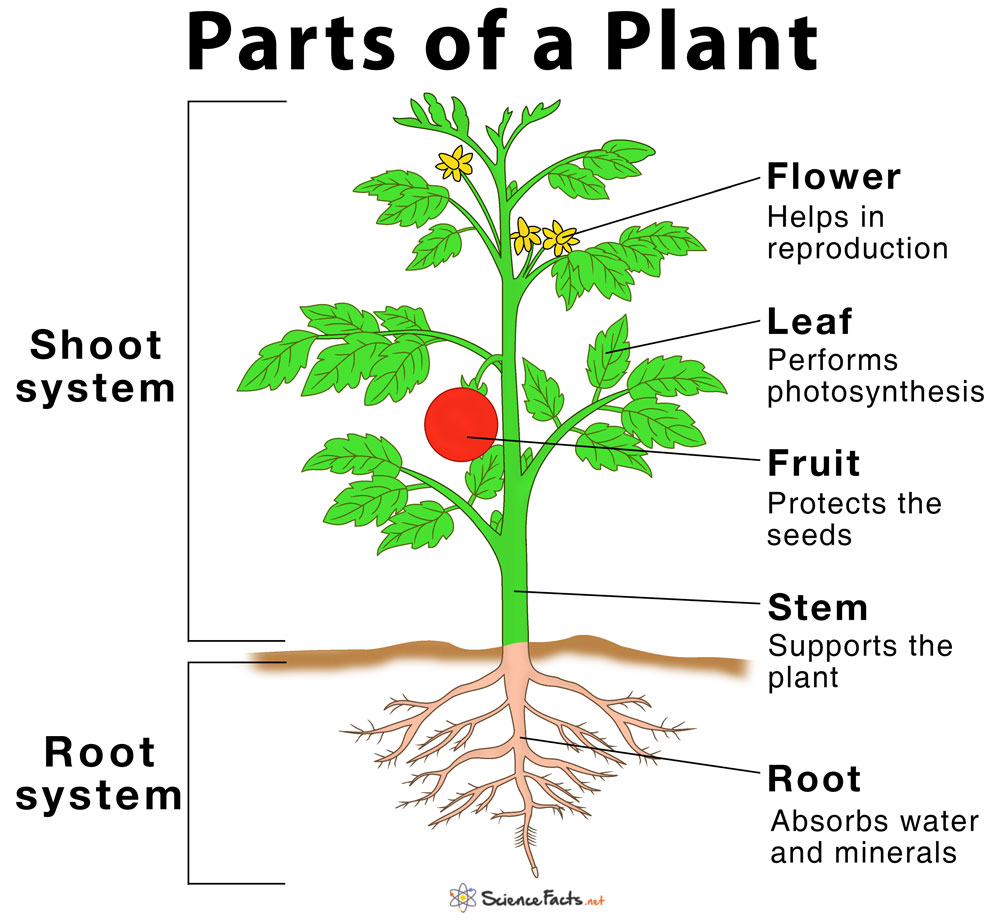
In this topic, children will learn the names of different parts of plants, and the jobs they do. The children will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate what plants need to grow well, and will present their findings to their classmates. Furthermore, they will have the chance to predict what will happen in an exciting investigation into the transportation of water within plants. They will work in a hands-on way to identify the parts of a flower, and will explore the different stages of the life cycle of a flowering plant.
Animals Including Humans
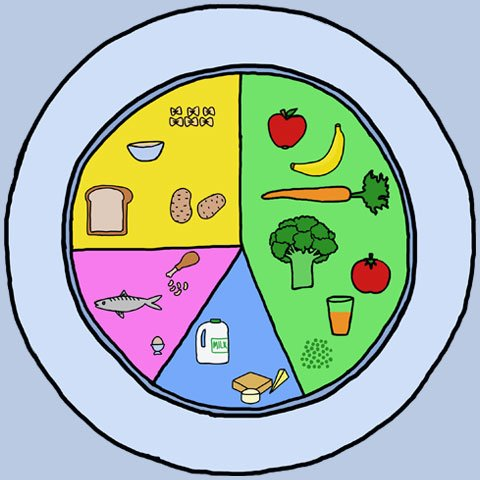
This unit recaps on the children’s learning from Year 2 about how animals survive and stay healthy and helps children to learn more about what makes a healthy, balanced diet. They learn about the nutrients that different foods provide and how these nutrients help our bodies. They also explore how different animals eat different types of foods and need different proportions of nutrients. They understand what food labels on packaging show and gather information from food labels to help them to answer questions. In this unit, children also explore the different types of skeletons that animals have and compare these. They learn some names of bones in the human body. They work scientifically by carrying out an investigation to explore if people with longer femurs jump further. They discuss how to plan a fair test and measure and record accurately. Children learn about how muscles help us to move and make a simple scientific model which they use to explain to a partner how skeletal muscles work.
Year 4
Animals Including Humans
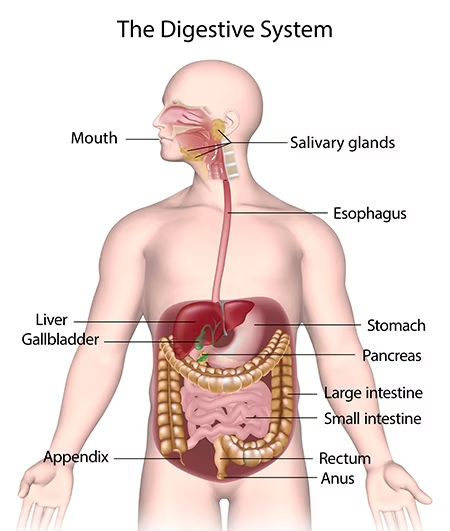
In this topic, children will expand on their learning from year 3 about how animals, including humans, need to get nutrition from what they eat. They will explore the different organs of the digestive system in humans and the functions of teeth in both humans and animals. Firstly, children will learn about the different types of teeth and the importance of good dental hygiene, before planning and carrying out an investigation into tooth decay using an egg as a model tooth. They will then learn about the parts and functions of individual organs of the human digestive system and carry out their own scientific demonstration of the process using everyday household items. Children will then learn more about herbivores, carnivores and omnivores in the context of teeth, digestion and food chains. They will extend their understanding of food chains from key stage 1 to include more complex chains, using the terms ‘consumers’ and ‘producers’ and compare food chains in different habitats. Finally, children will compare the teeth of different types of animals and apply their understanding to make links with their role in the food chain.
Electricity
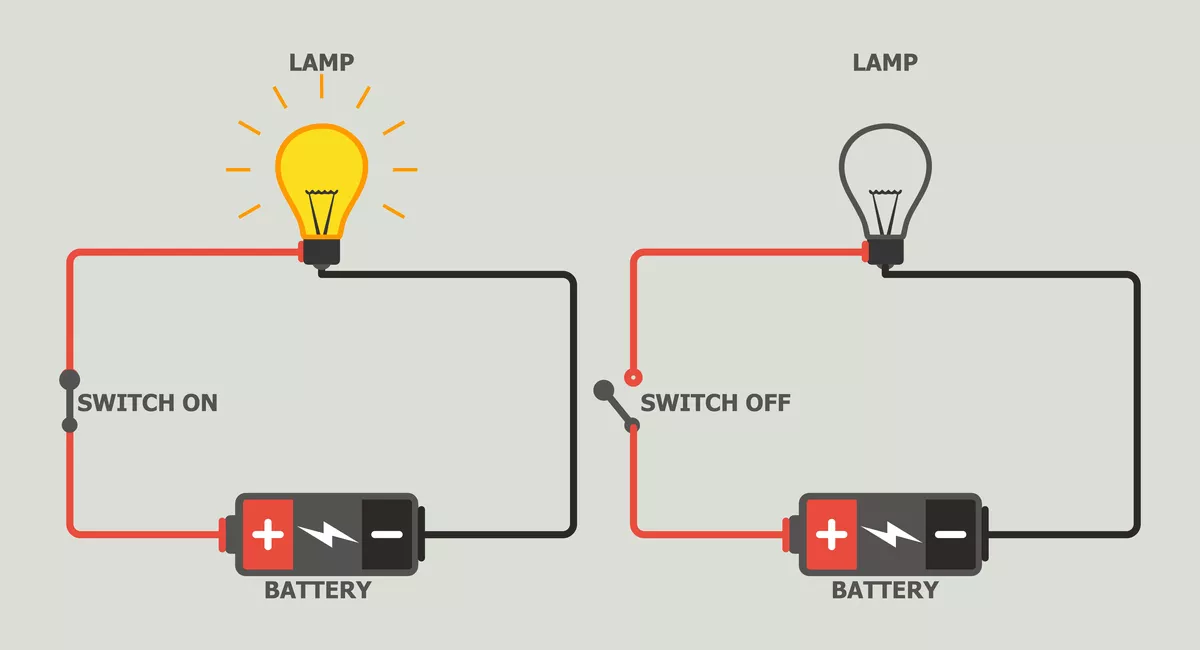
Here we will learn about common electrical appliances and how to construct simple series circuits. They will become familiar with the key words linked to the topic and how to apply them appropriately. Children will learn about cells, wires, bulbs and buzzers and about the different types of switches. They will be able to troubleshoot and identify whether or not a bulb will light in a simple series circuit and be able to identify a complete circuit. The children will also learn about conductors and insulators and know that metals are very good electrical conductors.
States of Matter
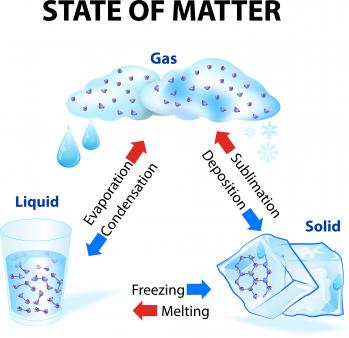
In this topic, we will learn about the differences between solids, liquids and gases, classifying objects and identifying their properties. The children will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate the weight of a gas. Furthermore, they will have the chance to find the ideal temperature to melt chocolate. They will explore in-depth how water changes state by exploring melting, freezing, condensing with a particular focus on evaporation. Finally, they will learn about the stages of the water cycle, creating mini water worlds and an exploring what happens to a balloon when it is blown up.
Living things and Habitats
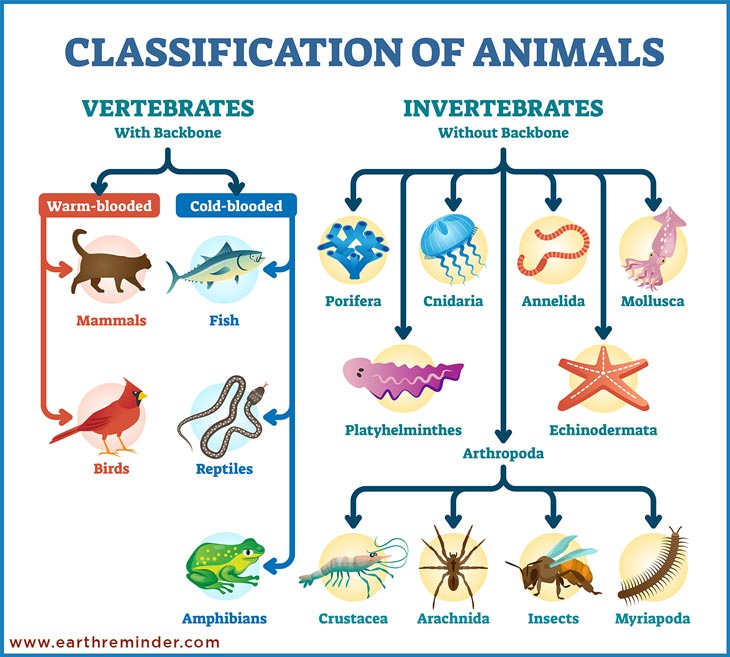
In this topic, children will explore a variety of ways to identify, sort, group and classify living things. They learn how animals are split into 'vertebrates' and 'invertebrates' and begin to consider the differences between living things within these classifications. They use and create classification keys to group, identify and name living things from the local habitat and beyond. They will be introduced to the idea that environments are subject to human-made and natural changes, and that these changes can have a significant impact on living things. Throughout this topic children work scientifically by gathering, recording and presenting information in different ways.
Sound

In this topic, children will learn about how vibrations cause sounds and how sounds travel, as well as how sounds can change pitch and loudness. The children will learn about how sounds are made, carrying out demonstrations of vibrations, and completing a sound survey of their school. They will work in groups to create a human model of the way particles pass sound vibrations on, and write, take photos and represent how sound travels. The children will work in a hands-on way to explore pitch, and will use their understanding of how high and low sounds are made to create their own instrument. They will have the opportunity to make a string telephone, and will use this to investigate how sounds change over distance and through different materials. The children will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate the best material for soundproofing, in the context of making a music studio quieter. Finally, they will demonstrate their learning from the whole unit by designing and creating their own musical instrument that will play high, low, loud and quiet sounds.
Years 5 & 6 Learning Journey
Year 5
Forces

In this topic, children will learn about types of forces such as gravity, friction, water resistance and air resistance. They will also learn about the use of mechanisms such as levers, gears and pulleys. The children will identify forces and find out about Isaac Newton and his discoveries about gravity. The children will look for patterns and links between the mass and weight of objects, using newton meters to measure the force of gravity. They will also work collaboratively to investigate air and water resistance, participating in challenges to design the best parachute and investigate how streamlined objects move. They will have the opportunity to work in a hands-on way to explore friction, developing their own brake pad for a tricycle or scooter. During some of the practical science work, the children will discuss how variables other than the one being tested can be kept the same to help make a test fair. Finally, they will find out about different mechanisms, including levers, gears and pulleys, and will design their own marvellous machine.
Properties and Changes of Materials
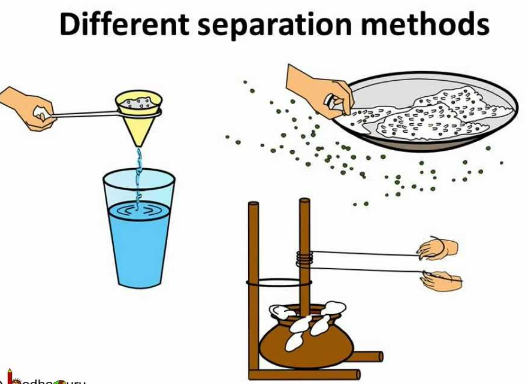
Here we will learn about different materials, their uses and their properties, as well as dissolving, separating mixtures and irreversible changes. The children will sort and classify objects according to their properties. They will explore the properties of materials to find the most suitable material for different purposes. The children will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate the best thermal insulator to make a lunch box, making predictions and forming conclusions. Furthermore, they will have the chance to find the best electrical conductor, in small circuits thinking about how to improve the intensity of a bulb. They will have the opportunity to work in a hands-on way to explore dissolving, identifying the different variables in their own investigations. They will find out about different ways to separate mixtures of materials, using filtering, sieving and evaporating. Finally, they will learn about irreversible changes, and participate in two exciting investigations to create new materials, including reversible changes.
Space
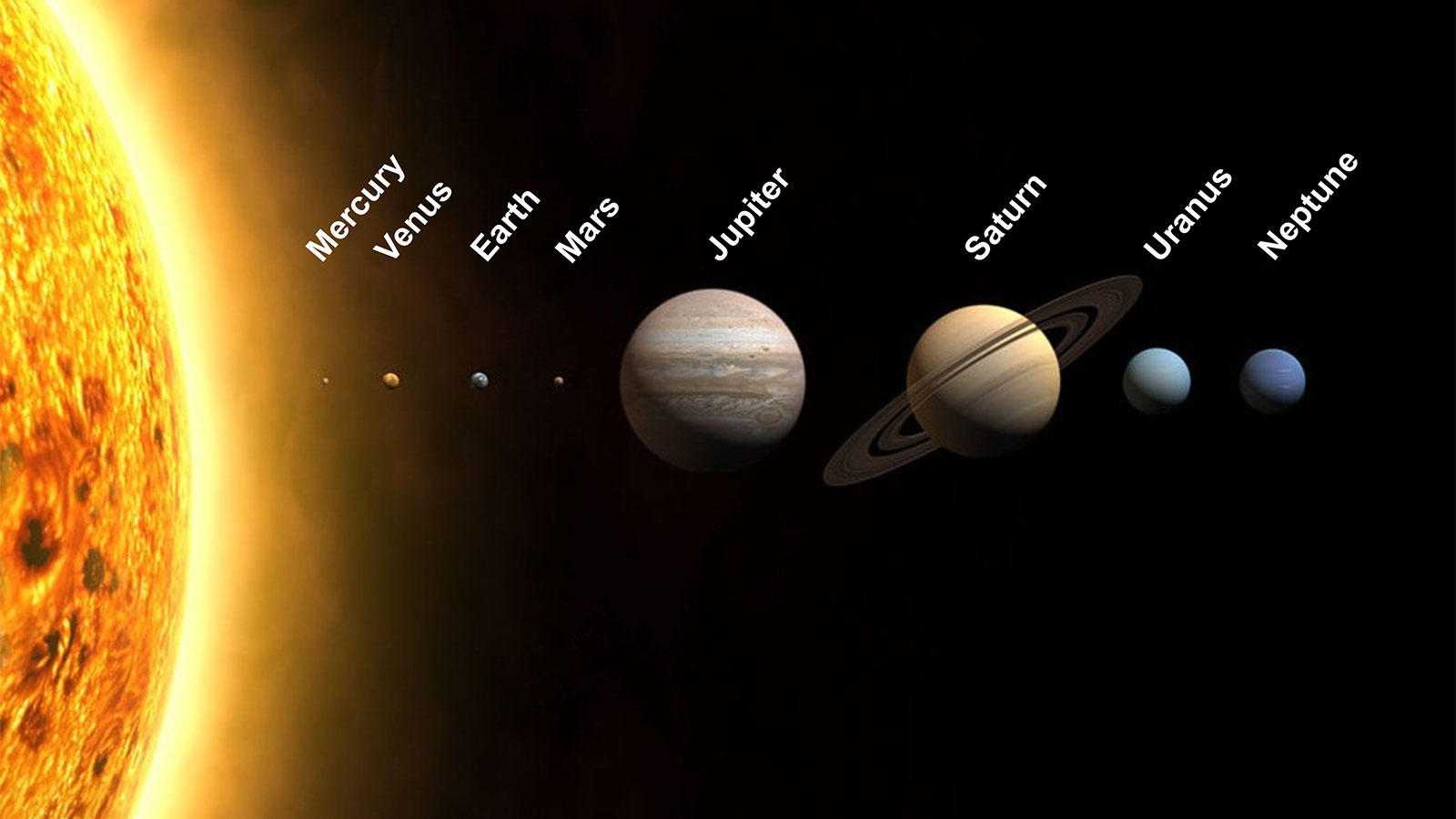
This topic is the only astronomy related science unit in the primary science curriculum. The aim is to give children a basic overview of Earth and its place in our Solar System Children will identify scientific evidence, learn and name the planets in the solar system, explain how the planets orbit the Sun, explain how night and day occur, make predictions about night and day in different places on Earth, report and present findings from enquiries and finally explain that the Moon orbits the Earth not the Sun.
Animals Including Humans
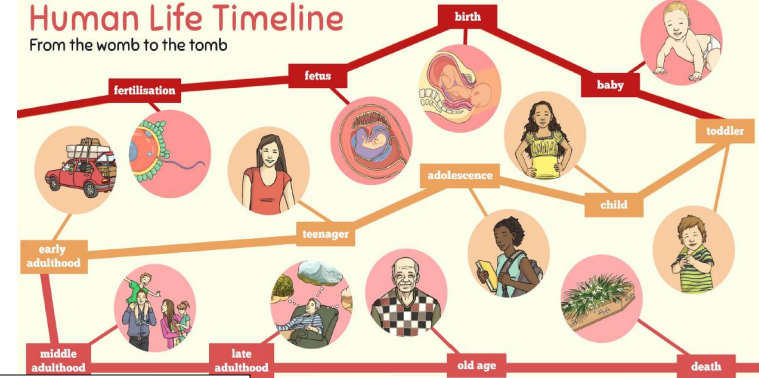
This topic focuses on the changes that human beings experience as they develop to old age. It tackles some sensitive subjects including puberty and death. Children will learn about the life cycle of a human being. They will investigate the development of babies and compare the gestation period of humans and other animals. They will learn about the changes experienced during puberty and why these occur. The final investigation will be about the changes to the body as humans get older, as well as comparing the life expectancy of different animals.
Living Things and their Habitats
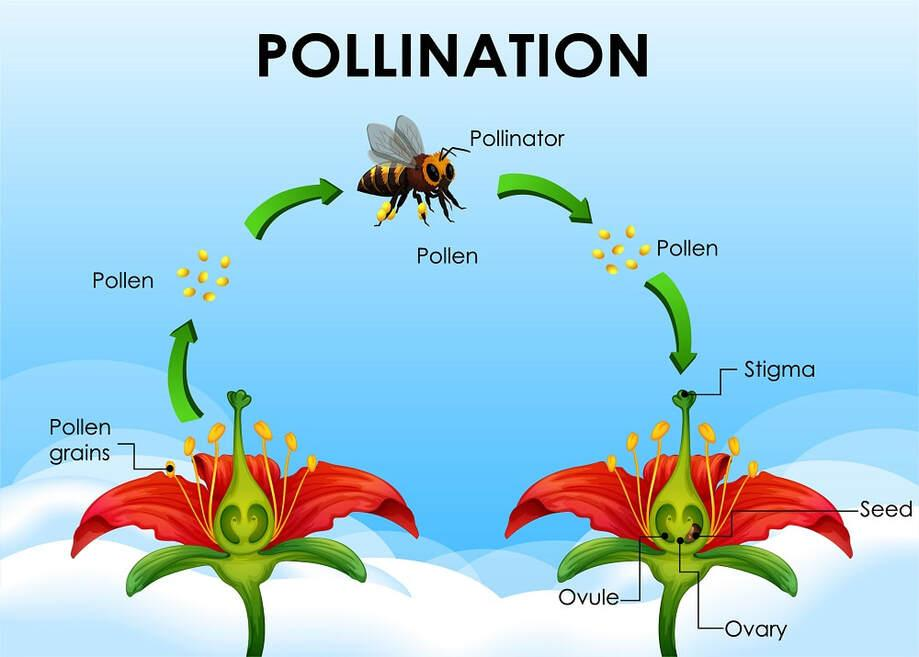
In this topic, children will learn about the process of reproduction and the life cycles of plants, mammals, amphibians, insects and birds. The children will explore reproduction in different plants, including different methods of pollination and asexual reproduction. They will recap their work in Year 3 by recapping the parts of a flower. They will learn about different types of mammals and their different life cycles, making life cycle wheels to present their learning. Furthermore, the children will find out about Jane Goodall and her work with the now-endangered chimpanzees in Africa. They will explore metamorphosis in insects and amphibians, comparing their life cycles. Finally, the children will explore the life cycles of birds, and will write and create their own wildlife web page comparing the life cycles of different living things.
Year 6
Animals Including Humans
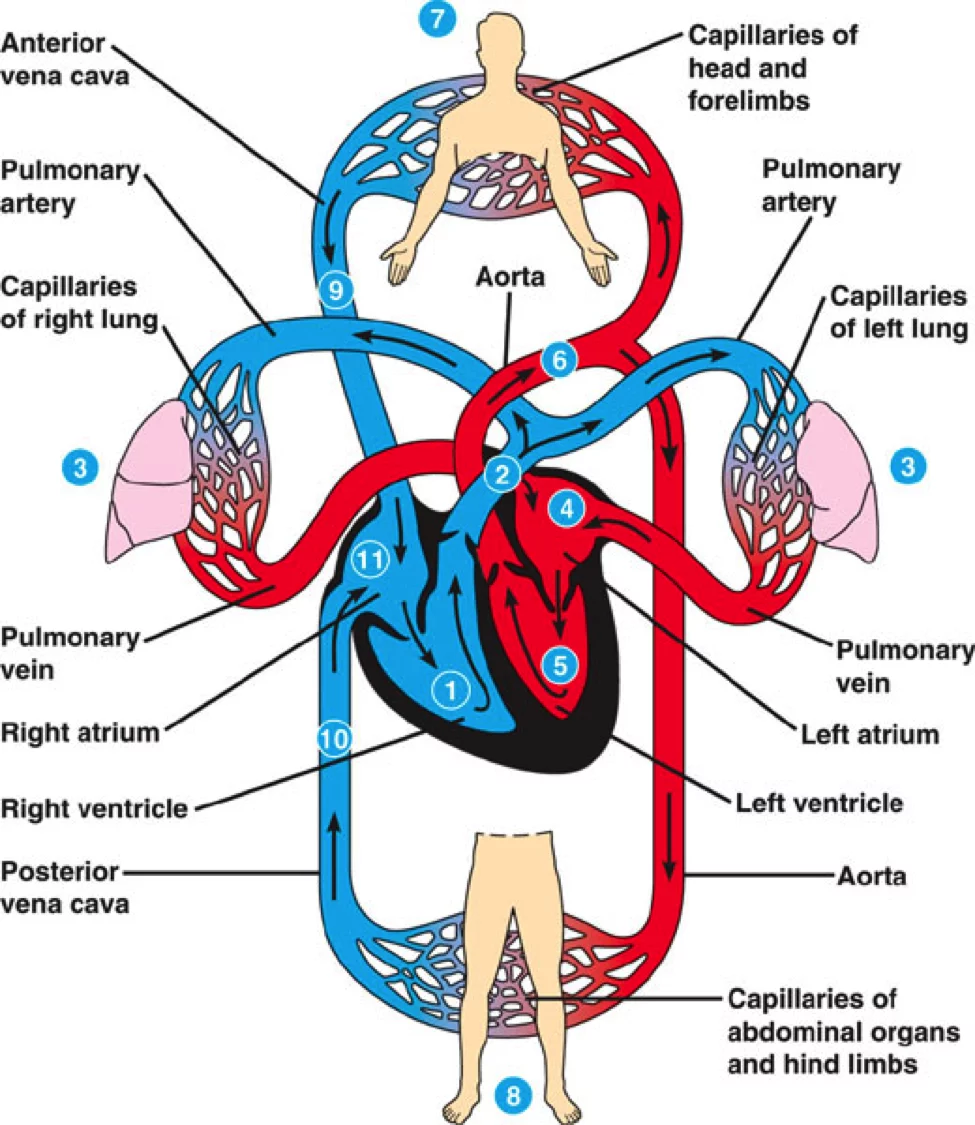
In this topic, children will recap on the learning from year 4 about how animals survive and stay healthy and learn more about how different organ systems work. They will learn the importance of diet, exercise and lifestyle in the way that bodies function. Children will learn about the three main parts of the circulatory system and the job of the heart. They also learn about what blood is comprised of and how it is transported around the body. Children carry out an investigation to explore how heart rate is affected by exercise. They discuss how to plan a fair test and measure and record accurately. Children learn the importance of exercise and conduct a survey to find the most popular exercise in their class. They then apply their understanding by discussing different people's lifestyles and how this can affect their bodies. Finally, children will learn about drugs and alcohol and how they can have an impact on our bodies, specifically in relation to the circulatory system.
Electricity
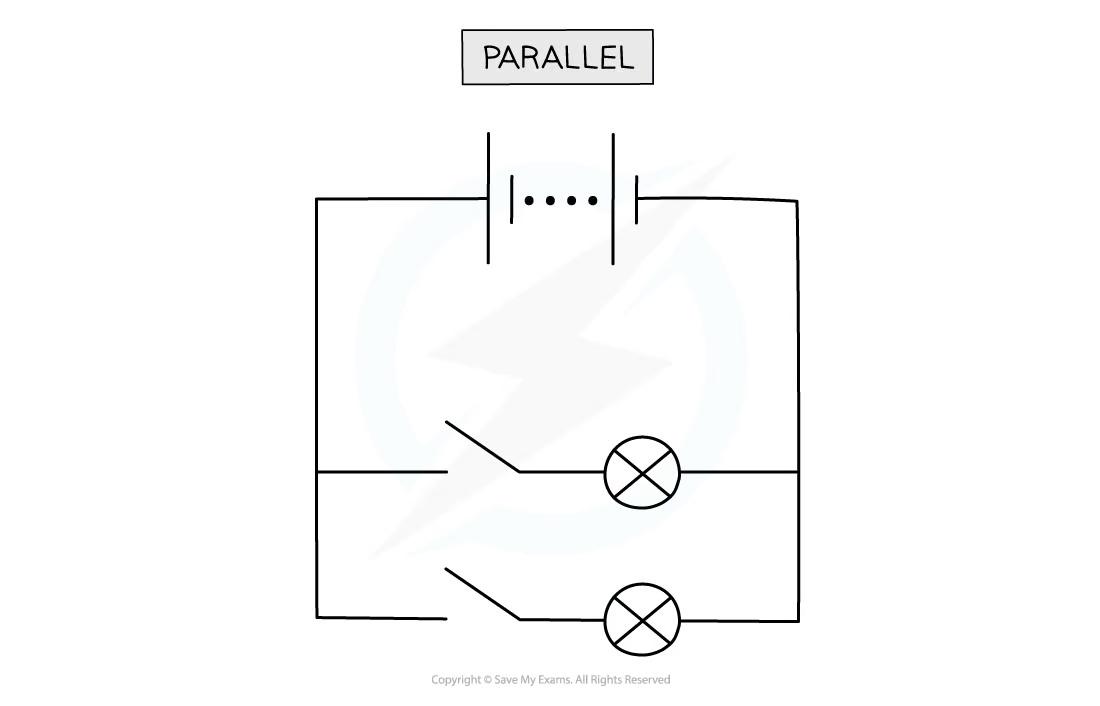
Here we will build on their learning from Year 4. Children will learn to represent circuits using symbols in a diagram. They will learn about two of the most important scientific inventors in the field of electricity – Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla. Children will get the opportunity to develop their understanding of what electricity is and how to measure it. As well as conducting their own investigation, they will get the opportunity to create their own torch!
Light

This topic will teach children how we see, shadows, reflection and refraction. The children will learn how light travels and how this enables us to see objects. They will demonstrate their knowledge by making and starring in their own television programme. The children will have the opportunity to make a functioning periscope, finding out about mirrors and the angles of reflection and incidence. They will work scientifically and collaboratively to investigate refraction, carrying out some fascinating experiments into the effects of bending light. Furthermore, they will have chance to predict what will happen in an exciting investigation into the visible spectrum. They will work in a hands-on way to explore how light creates the colours we see, designing coded messages. Finally, they will learn about Isaac Newton and his theory of light and colour, performing a shadow puppet play about his discoveries and ideas.
Living Things and their Habitats
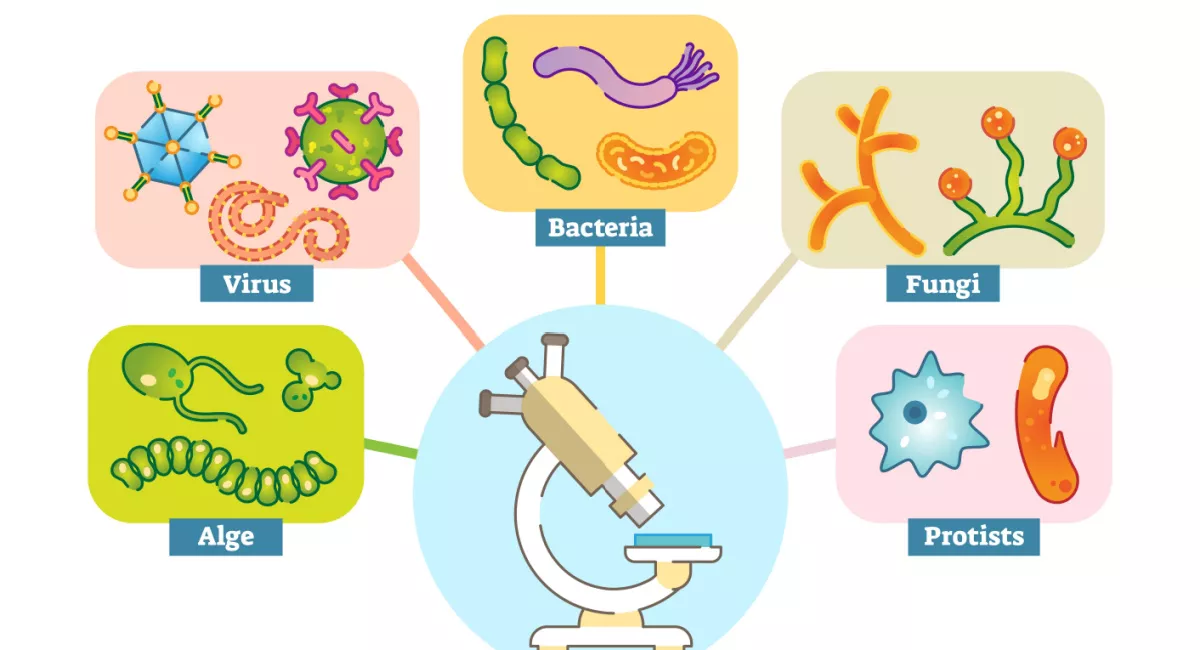
This topic focuses on the classification of living things, including micro-organisms. The children will build on their work in Year 4 by sorting animals into groups based on their similarities and differences. They will extend their learning to find out about the standard system of classification first developed by Carl Linnaeus, choosing an animal and researching its classification. The children will have the opportunity to design their own ‘curious creature’ and classify it based on its characteristics. They will learn about micro-organisms, and conduct an investigation into the growth of mould on bread. Furthermore, the children will use play dough to create a new single celled micro-organism and explain how it is classified and why. Finally, the children will put their learning into practice by creating a field guide to the living things in their local area, showing how and why each one is classified.
Evolution and Inheritance

In this topic, children will build on the learning from Year 3 Rocks unit as well as the Animals including Humans and Living Things and their Habitats units. Children will need to have a good understanding of fossils, habitats and human development in order to grasp the concepts and ideas presented to them in these lessons. Children will learn about variation and adaptation. They will be able to explore how both Charles Darwin and Alfred Wallace separately developed their theories of evolution. They will examine the scientific evidence from plants and animals that has been gathered to support the theory of evolution.
